Oracle Fusion Middleware
This Blog contains some Proof of Concepts related to Oracle Fusion Middleware Technology Stack
Tuesday, January 4, 2022
Saturday, April 21, 2018
User Personalization With MDS in Oracle ADF
(ADF/JDeveloper/Weblogic
12.2.1.3, Oracle Database 12.1.0.2)
In this post, I want to list the steps involved in setting
up the User Personalization Configuration for an ADF Application with MDS
Repository in the Database.
This is all documented very well in Oracle Documentation and
a lot of blog posts, but most of the information is scattered across different
sources. The errors which are encountered while implementing this may not give
much information to find out the actual issue and it can be sometimes frustrating.
The error is mentioned in point 7 below.
In this post I will try to put all of the steps together so
that anyone who is trying to do this for the first time will find it easy to
implement it. I personally found it difficult to find what I was missing and it
took a lot of research and help form others to get this working. This
particular gap I am mentioning below in the steps 4 and 5
Assuming that you have already done the following ***
ADF Application is enabled with Security
Deployed on a clustered Weblogic
Server environment
MDS Repository is already created
Data Source is configured in
Weblogic Console.
Personalization will work only if security is enabled as the
personalizations are stored against each authenticated user.
1.
First we need to enable the User Customization
Settings in the View Controller Project Properties
2.
Then we need to enable the MDS Customization
Settings for the ADF Application
This should be done in adf-config.xml file
We may have to go to the source of the file
to change the XML as below for the section ‘adf-mds-config’
<adf-mds-config
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
<mds-config
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/mds/config"
version="11.1.1.000">
<cust-config>
<match
path="/">
<customization-class
name="oracle.adf.share.config.UserCC"/>
</match>
</cust-config>
<persistence-config>
<metadata-namespaces>
<namespace
path="/persdef" metadata-store-usage="MAR_TargetRepos"/>
</metadata-namespaces>
<metadata-store-usages>
<metadata-store-usage
id="MAR_TargetRepos" deploy-target="true"
default-cust-store="true">
<metadata-store
class-name="oracle.mds.persistence.stores.db.DBMetadataStore">
<property
name="jndi-datasource" value="jdbc/mds/DEV_MDS"/>
<property name="repository-name"
value="mds-APP_MDS"/>
<property
name="partition-name" value="APP_PARTITION"/>
</metadata-store>
</metadata-store-usage>
</metadata-store-usages>
</persistence-config>
</mds-config>
</adf-mds-config>
3.
Select the ADF Faces Components you want the
User Personalization to be enabled for
At this stage when we run the application
in JDeveloper with Integrated WLS, it may work well as it might use the File
based configuration for storing the user personalization settings.
But if you are using an Ant Build Script or
Deploy the application from WLS console to a clustered server, then you will have to do one more
additional step. And this was what I was missing and took me a while to figure.
4.
We need to create and register a Metadata
Repository along with a Partition for the Application
This can be done either manually at the
command prompt or using a ‘python’ script.
For this we need to use the Weblogic
Scripting Utility that comes along with the JDeveloper installation.
C:\app\oracle\Middleware\jdev12213\oracle_common\common\bin\wlst.cmd
When we run this utility it will give us a
set of APIs to call to create and register the repository.
The general steps involved are as follows
Connect
Register
Metadata Repository
Create
Partition
For Example
connect(<WLS Admin User>, <WLS
Admin Pwd>, <WLS Admin Console
URL>)
registerMetadataDBRepository(name='mds-APP_MDS',
dbVendor='ORACLE', host=<WLS Host>, port=<WLS Port>,
dbName=<DB
Service Name>, user=<DB Username>, password=<DB Password>,
targetServers=<Cluster Name>);
createMetadataPartition('mds-APP_MDS',
'APP_PARTITION');
exit()
This can be run on any machine as long as
we give the correct server parameters
This is typically a one time operation.
5.
Update the Application EAR file with the
Metadata Repository information
Once the application EAR file is built, we
need to update the EAR file with the MDS Repository and Partition Information.
For this also, we need to use the WLST commands or write a python script.
The general steps involved are as follows
Connect
Open EAR file
Set
Application Metadata Repository Information
Save the EAR
file
For Example
connect(<WLS Admin User>,
<WLS Admin Pwd>, <WLS Admin
Console URL>)
archive = getMDSArchiveConfig(fromLocation=<EAR
File Path>)
archive.setAppMetadataRepository(repository='mds-APP_MDS',
partition='APP_PARTITION', type='DB',
jndi='jdbc/mds/APP_MDS')
archive.save()
6.
Now, the EAR file is ready to be deployed to a
clustered server with User Personalizations enabled with MDS Repository
7.
Error when deploying without updating the EAR
file
[exec]
weblogic.deploy.api.tools.deployer.DeployerException: Task 0 failed: [Deployer:149026]deploy
application APP on DefaultServer.
[exec] Target state: deploy failed on
Server DefaultServer
[exec]
weblogic.application.ModuleException:
oracle.mds.config.MDSConfigurationException: MDS-01335: namespace
"/persdef" mapped to metadata-store-usage "MAR_TargetRepos"
but its definition was not found in MDS configuration.
:oracle.mds.config.MDSConfigurationException:MDS-01335: namespace
"/persdef" mapped to metadata-store-usage "MAR_TargetRepos"
but its definition was not found in MDS configuration.
[exec] at
oracle.mds.config.PConfig.populateNamespaceConfigList(PConfig.java:1499)
[exec] at
oracle.mds.config.PConfig.loadFromBean(PConfig.java:1166)
[exec] at
oracle.mds.config.PConfig.<init>(PConfig.java:892)
[exec] at
oracle.mds.config.MDSConfig.loadFromBean(MDSConfig.java:1288)
[exec] at
oracle.mds.config.MDSConfig.loadFromElement(MDSConfig.java:1360)
[exec] at
oracle.mds.config.MDSConfig.<init>(MDSConfig.java:905)
……
8.
Reason for the above error is that even though
we have added the MDS Configuration in the adf-config.xml file, when the EAR is
built initially, this entry will be removed by Ant. This is the expected
behavior according to oracle documentation.
So we are supposed to perform the
additional step I mentioned in the step 5 to update the EAR file with the
repository information.
9.
Some Observations
a.
User Personalization Settings will persist
across multiple deployments of the application
b.
The EAR file size that is updated by the WLST
API in the step 5 is much lesser than the original EAR
c.
Once the User starts personalizing the pages,
after that if we make changes to the adf-config.xml to remove some components
from personalization, the change does not seem to be effective.
Friday, April 20, 2018
Sub Query Workarounds for ADF View Object Design Time Issues in JDeveloper
ADF/JDeveloper 12.2.1.3
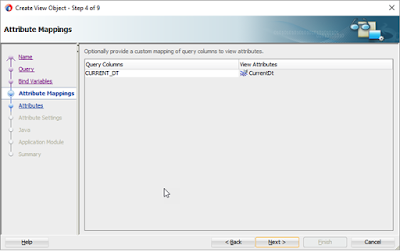
In this blog, I will show some workarounds for some specific issues we may see in JDeveloper View Object Wizard
When we are designing a View Object in JDeveloper, especially when we modify the query in the expert mode, in some cases as mentioned below, the wizard does not build the attribute mappings as expected.
- When the Query has an 'extract' clause
- When the Query has a table or view accessed from a DBLink
- When the Query has a synonym for an object from another Schema
We normally see this behavior when we join attributes from tables with one of the above.
A General Workaround for these kind of issues is to use
a Sub Query.
- When we use Extract clause in the query to get an attribute, the attribute is not shown as a selected attribute in the Attribute Mappings. This issue comes especially when we join the ‘extract’ attribute with other attributes
- When we query a table via a DB Link the attributes from the DB Link are not shown in the ‘Attribute Mappings’. This issue comes especially when we join the ‘dblink’ attributes with other attributes
- When we query columns from a partitioned table the attributes are not shown in the Attribute Mappings. Below table is partitioned on ‘payroll_date’.This happens especially when we join the attributes with other table attributes.Other best option in this case is if the table is in a different Schema, then we may have to give the Owner Schema Prefix also
Thursday, May 14, 2015
Shared ADF Libraries Within One Application
(JDeveloper
12.1.3, WLS 12.1.3)
This
post is inspired from the original post by Andrejus Deploying ADF Applications as Shared Libraries on WLS.
I
tried to do the same thing but the only difference is that I tried to keep all
the code in one single ADF application.
I
think this will keep all code related to the whole application in one place in
source control, so maintenance will be easy.
This
will also eliminate the necessity of the SharedLib intermediate Application.
And
we can deploy the shared libraries changes individually without affecting other
parts of the application.
And
ofcourse these shared libraries can be accessed from a different ADF
application as well.
Departments
and Jobs ViewController projects are deployed as Shared ADF Libraries.
HRDashboard
project is the main project which will use the two libraries.
Create
2 Deployment profiles in Departments and Jobs ViewController projects as shown
below, one an ADF Library Jar profile and another WAR profile.
In
the HRDashboard Project, create a weblogic.xml deployment descriptor to add the
2 shared libraries we created above in the Departments and Jobs projects. The
names should be same as the WAR profile names.
Add
both the library jar files to the HRDashboard project.
Create
a WAR deployment profile for the HRDashboard project.
Remove
the Contributors for Departments and Jobs in the Library filters of the WAR
deployment profile.
Create
an EAR Application Deployment Profile by selecting only the HRDashboard WAR
deployment profile in Application Assembly.
Deployment
Sequence
1.
Deploy both the Departments and Jobs ADF Library profiles to build the JAR files.
2.
Deploy both the Departments and Jobs WAR profiles to the Weblogic
server as Shared Libraries.
3. Deploy the EAR profile to the Weblogic Server as a
standalone application.
Note : It looks like we have to Stop the main
Application in the Weblogic Console when we are redeploying any of the shared
libraries, otherwise it will not allow us to deploy the shared libraries. We
can start it as usual when the shared library deployment is completed.
Friday, October 17, 2014
Human Task Assignees
(JDeveloper 12.1.3,
WLS 12.1.3, SOA/BPM Suite 12.1.3)
In this blog, I will show some
of many possible ways to assign a
Human Task to one or more Assignees and observe their behavior.
If a task has to be assigned
to more than one user, the simplest way is to assign it to a Group, but only if
all the users are in that Group. But if there are some users in the group which
the task should not be assigned to, or not all the users are present in the
group, then assigning the task to a Group may not work exactly how we want it to.
In such cases we can set the
assignees to a task in any of the following ways.
1.
Separate Parallel
Participants within same Stage
We
can modify the Human Task Assignees to add a new Participant as shown below. In
this example, I will set the first participant to be derived from the Swimlane. (User is assigned in Organization file)
And
the second participant to be derived from the payload.
Both
the above assignees are defined in the same stage, so considered to be
Parallel. That means the task will be assigned to both the assignees at the
same time.
When
one of the assignees responds to the task, the task is still assigned to the
second user and is not automatically completed.
The
second user also has to complete the task, only then the whole human task is set
to completed status. After the second user completes the task, below is the
human task status.
Note
that the ‘Voting’ concept is not applicable here since the task assignee Type
is still ‘Single’. So the human task is not completed until all the assignees
complete their tasks. (Voting is applicable when the Assignee Type is
‘Parallel’)
Also,
Note that ‘Claim’ also will not be applicable here. Even if the first user
Claims the task, the second user also have to submit the task. Until then, the
human task is not set to completed status. (Claim is applicable when assigned
to a Group or a comma separated users)
2.
Separate Serial
Participants within same Stage
For
this I will just change the participants sequence as shown below.
In this case when the task is created, the task will be first assigned to the Participant1.
Only
when first participant submits, the task will be then assigned to the
Participant2.
Only
when all the assignees in the chain submit their tasks, the human task is set
to completed status.
3.
Task Assignee Participant
Type : Parallel
For
this I will change the Participant type to ‘Parallel’ and get both the
assignees from the Payload.
In this, the task will be
assigned to all the assignees at the same time.
For
Parallel type of assignee, we can specify the task completion condition by vote
percentage in the Voting tab.
Following
condition means that if 50% of the assignees vote, irrespective of the outcome,
the human task is said to be completed.
For example, if we set the following condition, and both the assignees select REJECT action, then the default outcome SUBMIT will be applied to the human task.
Note
that the ‘Claim’ option is not available for the assignee in this case.
4.
Task Assignee
Participant Type : Serial
Works
similar to 2. (Separate Serial Participants within same Stage)
5.
Comma
Separated Users
For
this I will set the participant from only one payload attribute, but pass a
comma separated assignee name value to it while calling the process.
In
this case also, the task is assigned to both the users at the same time.
Note
that the Claim option is available to the users in this case.
When
one user ‘Claims’ the task, the other user will only be able to see the task in
his queue but will not be able to perform any actions on the task.
When
any one of the users submits the task, the human task is completed and is
removed from the other users Queue.
It is logically similar to
the behavior when both the users are in a Group and the task is assigned to the
Group.
6.
Group
Assignees
For
this I created a group ‘sdarbhaGroup’ in WLS and added 2 users sdarbha1 and
sdarbha2 in the group.
The
behavior is similar to 5. (Comma Separated Users)
7.
Complex
Assignees
This
is a very powerful way to set assignees based on complex business requirements.
Let
us assume that a particular human task has to be performed by many users with
different business responsibilities and in a particular sequence etc.
For
example, a task has to be completed by a data entry operator who enters some
basic information, then has to be assigned to 2 of his peers and a group for
review, and further has to be sent over a management chain, and finally a notification
to the administrator.
First assign it to a data
entry operator.
Then
assign it to his 2 peers.
Along
with a group at the same time.
Then
send it to a management chain for review.
And
finally send a notification to the Administrator.
When the task is generated following is the sequence of assignees.
The
Final FYI Notification will not be visible in the task flow audit trail, but is
sent to the administrator and will be visible in the BPM Workspace.
8. Multiple
Participants of different types in a Single Task Assignee Type
We can
also assign the task to multiple users, groups and application roles,
keeping the Assignee type as Single.
In this case the task will be assigned to all the users, users in the group,
and users from the application at the same time.
Any one from the above users can claim the task and work on it.
The task will be marked as completed when one user submits the task.
9. Multiple
Participants of different types in a Serial Task Assignee Type
We can
also assign the task to multiple users, groups and application roles,
keeping
the Assignee type as Serial.
In this case first the task will be assigned to sdarbha3 only.
When he submits, then only the task will be assigned to sdarbha4.
Even though the users sdarbha3, sdarbha4 are assigned at the same time in the task definition, when the task is created, they will be assigned one after the other since the task type is Serial.
But, the task is assigned to the group, all the users in the task will be assigned at the same time and anyone can claim the task and work on it.
Saturday, August 23, 2014
Creating and Executing Test Cases for BPM Processes
(JDeveloper 12.1.3 / WLS
12.1.3 / SOA/BPM Suite 12.1.3)
In this post I will show how to create and execute Test
Cases for BPM Processes.
I will be using the same project which I used to show how to
define Business Rules in BPM.
http://sameerdarbha.blogspot.com/2013/07/implementing-business-rules-in-bpm.html
The above project was created in 11.1.1.7 version of BPM.
For this post, I will be using JDeveloper/BPM Suite/WLS 12.1.3.
I have migrated the application ‘EmployeeTravelExpenseSystem’
to 12.1.3.
And I modified the process a little bit to add another Start
activity of type ‘Message’ so that we can start and test this process from EM
console. It takes the input as the same object ‘TravelExpenseObject’ as shown
below.
Right click on ‘SOA > testsuites’ to create a Test Suite
as shown below and give a name to the Test Suite.
Right click on the Test Suite ‘ETEAPTestSuite’ and create a
Test case ‘AutoApprovalTestCase’
A new file ‘AutoApprovalTestCase.xml’ file will be created as
shown below which looks like the composite.xml
Create another test ‘RequiredApprovalTestCase’ with the
input xml as follows satisfying the Required
Approval case according to the Business rules.
We can run the individual Test cases or even the complete Test
Suite from within JDeveloper.
Right click the Test Suite name and select ‘Run Test Suite’.
JDeveloper will ask for the server name to which this
application has to be deployed. Enter the name of the server.
Also these test case execution results can be seen in the EM console.
This application is deployed to a 'Compact Domain' in the WLS.
Optionally the test cases also can be run on the EM console,
since the test cases are deployed along with the application.
When the Test Suite is run, 1 instance of the process for
each test case is created.
The instances created by the Automated Test Cases like this will be shown with a yellow 'dot'.
The instances created by the Automated Test Cases like this will be shown with a yellow 'dot'.
The Test case for Auto approval process flow is as follows.
The test case for Approval required process flow is as
follows.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)